Kamon Thinsurat, Zhiwei Ma, Anthony Paul Roskilly and Huashan Bao
Abstract:
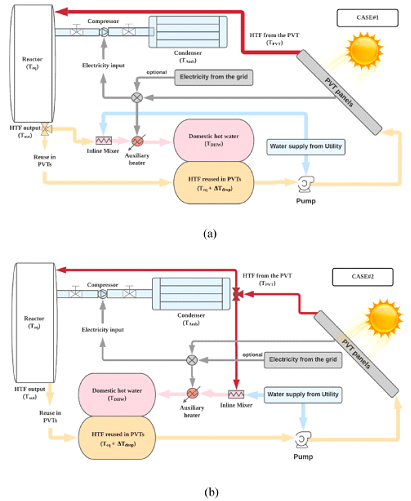
This paper studied the performance of a compressor-assisted thermochemical sorption energy storage (CATSES) system with a solar photovoltaic-thermal collector (PV/T) to support the domestic space and hot water heating. The heat from the PV/T drives endothermic desorption, whilst the electricity from the PV/T powers the compressor to assist the low-temperature desorption. The main aim of this study was to demonstrate that the integrated system can flexibly and maximally utilise solar energy, and store solar energy in a high energy–density system with minimum loss over long-term storage. The parametric investigation on the CATSES system using SrCl2/NH3 working pair was conducted for a case study in the city of Newcastle upon Tyne in the UK, which has long wintertime with high heating demand. Two different system operation modes (Case 1 and Case 2) with different strategies of solar energy usage (direct usage / storage) were studied. By using 30 m2 PV/T collector with the CATSES reactor that contains 22 m3 (450 kg/m3) composite adsorbent and a compressor with 11.5 compression ratio, the system that operated Case 1 could achieve 100% solar fraction of annual heating demand. The achieved material-based energy storage density was around 0.6 GJ/m3 and the storage efficiency was 0.88 with the net electricity consumption of 180 kWh (around 5% average consumption of an ordinary UK household). The system that operated Case 2 stored less heat than that of the Case 1 but was able to output more electricity.